Subscribe to this page via e-mail here - Subscribe
Article 38 - The World Of The New Testament
The World of the New Testament
"The New Testament cannot be adequately interpreted if approached as a collection of independent oracles handed down from heaven, without any reference to the human experience and environment amid which it was written. It is, indeed, the divine revelation of redemption, but this revelation did not arise as a product independent of historical relations. God was pleased to reveal his redemption in and through history, and we are not able rightly to comprehend that revelation until we approach it from the historical side. The New Testament is God's redemptive truth mediated to men through human experience. When viewed in this light it is best understood and yields its richest treasures." (H.E. Dana, The New Testament World, pp.9,10)
Note: The word "tribute" found in Matt. 17:24-27 is not the Roman tribute, but probably collections taken by Jewish officials.
III. DOCETICS (unnamed)
IV. WORLDLY (FALSE) WISDOM (random references) -- (Rom. 1:20-22; I Cor. 1:22-29; 2:1-8; 3:18-20; Col. 2:8; I Tim. 6:20,21)
VI. ANIMAL WORSHIP -- (Rom. 1:21-23)
VII. GENERAL IDOLATRY -- (Acts 15:20,29; 21:25; I Cor. 8:1-13; 10:14,19,20, 28,29; II Cor. 6:16,17; Gal. 5:19,20; I Thess. 1:9)
II. DIVINATIONS -- (Acts 16:16-19)
I. JEWS WERE DISPERSED THROUGHOUT THE ROMAN EMPIRE -- (Acts 2:9-11; 18:1,2)
VI. FEASTS
XVI. FALL OF JUDAISM
Print

The World of the New Testament
(The World at the Time of Christ and the Early Church)
Jon Gary Williams
Introduction
The New Testament is often identified with the first century A.D., for it was during this historical setting that the events found in the New Testament developed.
The New Testament is a record of the unfolding of God's plan within both Jewish and pagan worlds. As it reveals the developing of this plan, it does so with the backdrop of a secular environment. Hence, in the New Testament we discover God's final, divinely recorded message to man, but within the framework of first century history.
"The New Testament cannot be adequately interpreted if approached as a collection of independent oracles handed down from heaven, without any reference to the human experience and environment amid which it was written. It is, indeed, the divine revelation of redemption, but this revelation did not arise as a product independent of historical relations. God was pleased to reveal his redemption in and through history, and we are not able rightly to comprehend that revelation until we approach it from the historical side. The New Testament is God's redemptive truth mediated to men through human experience. When viewed in this light it is best understood and yields its richest treasures." (H.E. Dana, The New Testament World, pp.9,10)
It has often been noted that much of what we read in the New Testament can be confirmed by secular history. There are a great many such examples. However, it can also be said that first century history can equally be confirmed by the New Testament. Much of what existed in the first century can be found right there in its twenty-seven books. Apart from secular history it is amazing how much we can know about what the first century world was like.
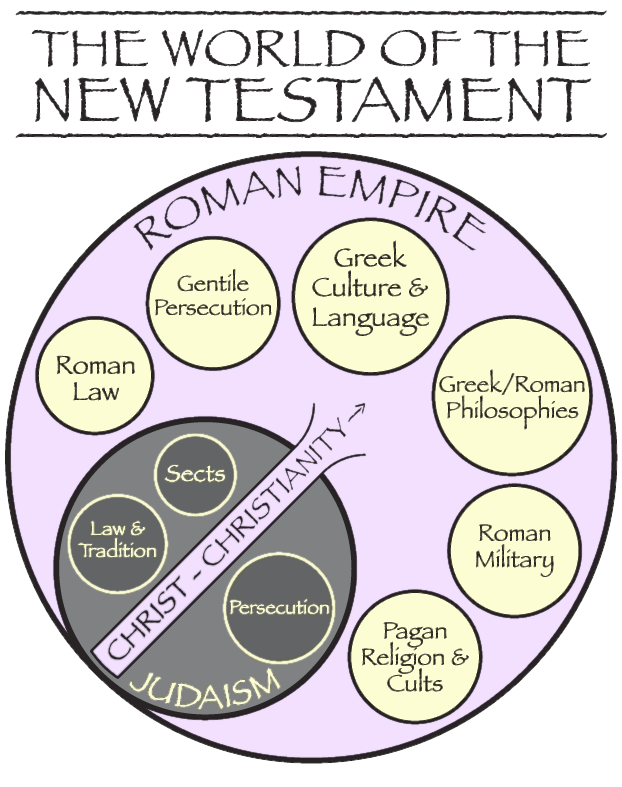
It is remarkable how precisely the story of the New Testament is interwoven with the history of its day. It is impossible to separate the record of the New Testament from first century people and events, which confirms the integrity of the scriptures. Within the New Testament there is abundant information about all avenues of life -- for example, in culture, government, law, language, philosophy, occupations, commerce and religious cults. These are found within both the Jewish and Roman worlds. The New Testament makes reference to a host of these. Find here in simple outline format the world of the first century found in the New Testament.
THE ROMAN EMPIRE
I. THE FOURTH WORLD GOVERNMENT (the broad picture)
A. Preceded by the Babylonian, Medo-Persian and Grecian Empires. (Dan. 2:31-33; 36-40)
B. Conquered the Grecian Empire in the 1st century B.C. and lasted from about 60 B.C. to 476 A.D.
C. Governed by emperors sharing power with the Senate.
II. TERRITORY
A. Began in Italy, rapidly spreading east and west.
B. At its peak it reached from the Atlantic Ocean to the Euphrates and from North Africa to Northern Europe.
III. GREEK INFLUENCE
A. Greek culture
1. "Grecians" -- referred to Jews from outside Palestine -- Acts 6:1; 9:29
2. "Greek" -- used to refer to all non-Jews -- Rom. 1:16; I Cor. 1:22,23; Col. 3:11. (In Rom. 2:9 & I Cor. 12:13, "Gentile" is used interchangeably with "Greek.)
3. Greek names were universally used -- Theophilus: Lk. 1:3; Aristarchus, Marcus: Col. 4:10; Timotheus: Acts 16:1; Gaius: III John; Tychicus: Eph. 6:21; Epaphroditus: Phil. 4:18; Archippus: Col. 4:17; Artemas: Tit. 3:12; Epaphras: Phile. 23; Silvanus: I Pet. 5:12; Diotrephes: II John 9 (see also Rom. 16:7-15)
B. Greek Thought
1. Philosophical heritage -- Plato, Aristotle, Anaximander, Anaximenes, Zeno, Epicurus, Philo, etc.
2. Some good came from Greek thought, but it also had its bad influence (I Cor. 3:18-20; Rom. 1:21,22)
C. Greek Language
1. Greek was the universal language of the Roman Empire.
2. The New Testament was written in "koine" (common) Greek. On Pentecost Peter spoke to Jews of different languages in this common language. (Acts 2:13-36)
3. "Alpha" and "Omega" were Greek words. Rev. 1:8,11; 21:6; 22:13
4. The sign on the cross was written "in letters of Greek and Latin and Hebrew" (Lk. 23:38) (cf. Jn. 19:20)
5. The Greek language told of a Jewish maiden (Mary) who gave birth to a boy (Jesus) under the rule of Roman law.
IV. GOVERNMENT OFFICIALS
A. Emperor
1. Augustus (Octavius - 27 B.C. - 14 A.D.) -- who ordered the census decree at the birth of Jesus. (Lk. 2:1-5) (see Acts 27:1; Matt. 22:17-21)
2. Tiberius (14 - 37 A.D.) -- emperor when John began his work and when Jesus was on trial. (Lk. 3:1; Jn. 19:12-15)
3. Claudius (41 - 54 A.D.) -- emperor during the world-wide famine and who commanded the Jews to leave Rome. (Acts 11:27,28; 18:1,2)
4. Nero (unnamed, 54-68 A.D.) -- to whom Paul appealed. (Acts 25:8-12, 21,25; 26:32; 27:23,24; 28:19: Phil. 4:22)
B. Governor (Procurator - ruler of an imperial province)
1. Cyrenius -- who was governor of Syria when the world-wide census was made. (Lk. 2:2)
2. Pilate -- before whom Jesus appeared. (Matt. 27:2, 17-26; Lk.13:1; Jn. 19:19-22, 38; Acts 3:13; 4:27; 13:28; I Tim. 6:13)
3. Felix -- before whom Paul appeared. (Acts 23:24, 33-35; 24:1, 10, 24-26)
4. Festus -- before whom Paul appeared. (Acts 24:27; 25:1-12)
5. Governor (unnamed) -- under the renegade king of Arabia, Aretas, who sought to arrest Paul at Damascus. (II Cor. 11:32, 33)
C. Deputy (Proconsul -- ruler of a senatorial province)
1. Sergius Paulus -- to whom Paul preached at Paphos. (Acts 13:7-12)
2. Gallio -- who was deputy over Achaia when the Jews made insurrection against Paul. (Acts 18:12-17)
D. King (Jewish - allowed to serve under Roman rule)
1. Herod the great -- who had children put to death when Jesus was a child. (Matt. 2:1-12,16)
2. Herod Archelaus -- tetrarch of Judea. (Matt. 2:22)
3. Herod Antipas -- tetrarch of Galilee who killed John and heard Jesus. (Matt. 14:1-12; Lk. 23:6-12; Lk. 13:31,32
4. Herod Philip -- tetrarch of Iturea/Trachonitis. (Lk. 3:1)
5. Herod Philip -- (Matt. 14:3; Mk. 6:17)
6. Lysanias -- tetrarch of Abilene. (Lk. 3:1)
7. Herod Agrippa I -- who killed James and imprisoned Peter and who suffered a violent death. (Acts 12:1-23)
8. Herod Agrippa II -- before whom Paul appeared. (Acts 25:13-26; 26:1-32)
9. Aretas -- renegade king of Arabia who controlled Damascus when Paul was being sought. (II Cor. 11:32)
E. Magistrate (local civil authority)
1. Unnamed -- who had Paul beaten. (Acts 16:19-39; cf. Rulers - Acts 17:6,8)
2. Obedience to them admonished. (Tit. 3:1) (In Lk. 12:11,58, a broader term is used -- rulers in general)
F. Publican (tax collector)
1. Matthew -- (Matt. 9:9-11; 10:3)
2. Zacchaeus -- (Lk. 19:2-8)
3. Random information -- (Matt. 5:46,47; 11:19; 18:17; 21:31,32; Lk. 7:29; 15:1,2; 18:9-14)G. Chamberlain (treasurer)
1. Blastus, treasurer of Herod Agrippa I -- (Acts 12:20)
2. Erastus, treasurer of Corinth -- (Rom. 16:23) (cf. Acts 19:22; II Tim. 4:20) In Acts 8:27 this treasurer was not within the Roman Empire. He was the treasurer of Candace, queen of Ethiopia.
H. Townclerk (record keeper) -- (Acts 19:35-41)
V. CENSUS (Enrollment) -- (Lk. 2:1-5; Acts 5:37)
VI. TRIBUTE (tax paid by subjugated nations) -- (Matt. 22:17-21; Lk. 23:2; Rom. 13:6)
Note: The word "tribute" found in Matt. 17:24-27 is not the Roman tribute, but probably collections taken by Jewish officials.
VII. MILITARY
A. Band -- 600 soldiers (ten bands to a legion)
1. Italian band -- (Acts 10:1)
2. Augustus band -- (Acts 27:1)
3. Band at Jerusalem (unnamed) -- (Matt. 27:27)
B. Chief captain (over a band) -- Claudias Lysias -- (Acts 23:26) (see Acts 21:31-38; 23:17-30; 24:7)
C. Centurion (over 100 men)
1. Cornelius, centurion at Caesarea -- (Acts 10:1-8, 22-25, 30-33)
2. Julius, centurion at Caesarea -- (Acts 27:1-3, 11, 42, 43)
3. Unnamed centurion at Capernaum -- (Lk. 7:1-10)
4. Unnamed centurion at Jerusalem -- (Matt. 27:54)
D. Captain of the guard (served high ranking officials) -- (Acts 28:16)
E. Soldier -- (Matt. 27:27-31; 28:12-15; Jn. 19:23,24,32-34; Acts 10:7; 12:6,18)
F. Quaternion (group of four soldiers) -- (Acts 12:4)
G. Horsemen -- (Acts 23:23)
H. Spearmen -- (Acts 23:23)
I. Keeper (guard of a jail facility) -- (Matt. 28:4; Acts 5:23; 12:6,19)
J. Serjeant (lector -- officer under magistrates) -- (Acts 16:35-38)
K. Jailer (chief officer of a prison) -- (Acts 16:23-36)
L. Armor and weaponry -- (Eph. 6:13-17)
VIII. CIVIL CONTROL
A. Corporal punishment
1. Barabas -- (Mk. 15:6-8)2. Peter -- (Acts 12:3-7,17)3. Paul -- (Acts 16:23-28; 25:27; 27:1,42; 28:16,17; II Cor. 6:4,5; 11:23; Eph.6:20)4. Andronicus and Junia -- (Rom. 16:7)
B. Capital punishment
1. Christ -- (Matt. 20:17-19; 27:31-50)2. John -- (Mk. 6:27-29)3. James -- (Acts 12:1,2)4. Theudas and Judas -- (Acts 5:36,37)5. The government was an avenger -- ("minister of God...beareth not the sword in vain...a revenger of wrath") -- (Rom. 13:3,4)
IX. CITIZENSHIP -- (Acts 21:39; 22:24-30)
X. COMMERCE -- (Acts 21:3; 27:2,6,38)
XI. TRAVEL
A. Beast -- (Lk. 10:33,34; Acts 23:24)
1. Horse -- (Acts 23:23) (cf. Jam. 3:3)2. Ass (colt) -- (Jn. 12:14,15)
B. Chariot -- (Acts 8:28,29, 38)
C. Ship -- (Mk. 3:9; 4:36-38; Jn. 6:24; 21:8; Acts 13:4; 14:26; 15:39; 18:18,21; 20:6,15,16; 21:3,5,6; 27:6-44)
XII. COINS
A. Mite (lepton, about 1 cent) -- (Mk. 12:42-44)
B. Farthing (assarion, about 2 cents) -- (Lk. 12:6)
C. Penny/pence (denarion, about 15 cents) -- (Matt. 18:28; 20:2,9,10,13;22:17-19)D. Piece of silver (drachme, about 20 cents) -- (Lk. 15:8,9; Matt. 26:15; 27:3; Acts 19:19)
E. Tribute (tax) money (didrachmon, about 35 cents) -- (Matt. 17:24)
F. Piece of money (stater, about 75 cents) -- (Matt. 17:27)
G. Pound (mina, about $20) -- (Lk. 19:12-21)
H. Talent (talanton, about $250) -- (Matt. 18:23,24; 25:14ff)
XIII. NON-RELIGIOUS, NON-GOVERNMENT OCCUPATIONS
A. Physician -- (Mk. 5:25,26; Col. 4:14) (cf. Matt. 9:12)
B. Tent Maker -- (Acts 18:3) (cf. Acts 20:34; I Cor. 4:12)
C. Textile Merchant -- (Acts 16:14)
D. Fisherman -- (Matt. 4:18,19) (cf. Jn. 21:3)
E. Inn keeper (host) -- (Lk. 2:7; 10:34,35)
F. Husbandman -- (Matt. 21:33) (cf. Jn. 15:1)
G. Coppersmith -- (II Tim. 4:14)
H. Silversmith -- (Acts 19:24,25)
I. Lawyer -- (Tit. 3:13)
J. Farmer -- (Matt. 22:5; Lk. 12:16)
K. Ship master (captain) -- (Acts 27:11); Shipmen (sailor) -- (Acts 27:27,30)
L. Pearl merchant -- (Matt. 13:45,46)
M. Tanner -- (Acts 9:43; 10:6,32)
N. Sower -- (Matt. 13:24,25); Reaper -- (Matt. 13:28-30)
O. Orator -- (Acts 24:1,2)
P. Vineyard laborer -- (Matt. 20:1ff)
Q. Carpenter -- (Matt. 13:55; Mk. 6:3)
R. Shepherd -- (Lk. 2:8,18) (cf. Jn. 10:11,14); (I Pet. 2:25; 5:4)
S. Seamstress -- (Acts 9:36,39)
T. Exchanger (banker) -- (Matt. 25:27)
U. Porter (door keeper) -- (Mk. 13:34)
V. Potter -- Rom. 9:21 (cf. Matt. 27:7,10)
W. Gardner -- (Jn. 20:15,16)
X. Steward (household manager) -- (Lk. 12:42; 16:1,3,8) (cf. I Cor. 4:1,2)
Y. Builder -- (Matt. 21:42) (cf. Eph. 2:20)
Z. Harlot -- (Lk. 15:30)
AA. Money changer -- (Mk. 11:15; Matt. 21:12)
BB. Oil merchant -- (Matt. 25:8,9)
CC. Swine keeper -- (Matt. 8:32,33)
DD. Fuller -- (Mk. 9:3)
XIV. SOCIAL CLASSES
A. Beggar -- (Mk. 10:46-52; Lk. 16:20,21; Acts 3:2)
B. Servant
1. Hired servant -- (Mk. 1:20; Lk. 15:17,19; 16:13; Jn. 10:12,13; Mk. 14:66,69)2. Bond servant -- (Matt. 8:9; Acts 10:7; Rom. 14:4; I Cor. 7:21; Eph. 6:5-7; Col. 4:1; I Tim. 6:1; Phile. 10-16; I Pet. 2:18) (cf. Rom. 1:1 Phil. 1:1)
C. Wealthy -- (Matt. 27:57; Lk. 18:18-23; 19:2; Jam. 2:6,7) (cf. Matt. 19:23,24; I Tim. 6:17-19)
D. Greek-Jew distinction -- (Acts 18:1,2; I Cor. 12:13; Gal. 3:28; Col. 3:11)
E. Barbarian, Scythian -- Col. 3:11 (cf. Rom. 1:14; I Cor. 14:11)
XV. SCHOOLS OF HIGHER LEARNING -- (Acts 19:9,10)
XVI. SPORTING EVENTS -- (I Cor. 9:24,25; II Tim. 2:5) (cf. Heb. 12:1)
XVII. MORAL CONDUCT -- (Rom. 1:26,27; I Cor. 6:9-11; Eph. 4:17-19, 22; 5:3; Col. 3:5-7; I Pet. 4:3,4)
XVIII. PERSECUTION (of Christians)
A. Non-state religions were viewed in two ways
1."Religo-licita" -- licensed religion (Judaism fell in this category)2."Religo-illicita" -- unlicensed religion (after being identified separate from Judaism, Christianity fell in this category)
B. Churches
1.Thessalonica -- (II Thess. 1:4-6)2. Smyrna -- (Rev. 2:10)
C. Individuals
1. Apostle James -- (Acts 12:1,2)2. Apostle Peter -- (Acts 12:3-5; II Pet. 1:13,14) (cf. Jn. 21:18,19)3. Apostle Paul -- (Acts 14:2,5; 16:19-24; I Cor. 15:32; II Cor. 6:5; Phil. 1:13,14; II Tim. 4:6)4. Apostle John -- (Rev. 1:9)5. Antipas -- (Rev. 2:13)6. Random references -- (II Tim. 2:12; I Pet. 1:6,7; 2:12, 19-21; 4:12-14,16)
PAGAN PHILOSOPHY, RELIGION AND CULTS
The world at the time of the New Testament was saturated with heathen influence. This influence is seen in the forms of pagan philosophies, religions and cults. As the Lord's church spread throughout the Roman Empire it encountered a number of these Godless beliefs and practices.
Pagan Philosophies
I. EPICUREANS AND STOICS -- (Acts 17:18-21)
II. NICOLATIANS (probably aligned with the "Gnostics") -- (Rev. 2:6,15)
III. DOCETICS (unnamed)
A. Believed that flesh was inherently sinful, hence, could not accept Jesus in the flesh as Deity. Had a corruptive influence on the church.
B. They were identified as "anti-christ" -- (I Jn. 2:18, 22; 4:3; II Jn. 7)
1. They existed when John wrote his epistles -- (I Jn. 4:3)2. There were many of them -- (I Jn. 2:18) (cf. I Jn. 4:4,5)
C. Other references -- (I Jn. 4:1,2; John 1:1-4,14)
IV. WORLDLY (FALSE) WISDOM (random references) -- (Rom. 1:20-22; I Cor. 1:22-29; 2:1-8; 3:18-20; Col. 2:8; I Tim. 6:20,21)
Pagan Religions
I. SAMARITANS -- (Jn. 4:20-22, 39-42) (cf. Jn. 8:48)
II. BEELZEBUB -- (Matt. 12:24-27) (cf. Lk. 11:15-19; Mk. 3:21,22)
III. JUPITER AND MERCURY (Greek gods) -- (Acts 14:12-18)
IV. ATHENIANS -- (Acts 17:22-31)
V. DIANA (Greek goddess) -- (Acts 19:23-34)
VI. ANIMAL WORSHIP -- (Rom. 1:21-23)
VII. GENERAL IDOLATRY -- (Acts 15:20,29; 21:25; I Cor. 8:1-13; 10:14,19,20, 28,29; II Cor. 6:16,17; Gal. 5:19,20; I Thess. 1:9)
Pagan Cults
I. SORCERY
A. Simon -- (Acts 8:9-11)B. Elymas -- (Acts 13:6-12)
II. DIVINATIONS -- (Acts 16:16-19)
III. EXORCISM -- (Acts 19:13-16)
IV. MAGIC -- (Acts 19:19)
JUDAISM
"As was characteristic of the Roman government in dealing with its provinces, the Jews were treated with generous considerations so long as they were submissive to Roman rule. Their religion became one of the legally recognized religions of the empire, which meant that it was protected by Roman authority. They were allowed to pursue their national and private affairs without interference as long as they maintained peace and remained loyal to Rome." (H.E. Dana, The New Testament World, pp. 91, 92)
I. JEWS WERE DISPERSED THROUGHOUT THE ROMAN EMPIRE -- (Acts 2:9-11; 18:1,2)
II. JEWISH TRIBES
A. Asher -- (Lk. 2:36)
B. Benjamin -- (Acts 13:21; Rom. 11:1)
C. Judah -- (Heb. 7:14) (cf. Rev. 5:5)
D. All the tribes -- (Rev. 7:4-8)
III. JEWISH INSTITUTIONS AND OFFICES
A. Council (Sanhedrin) -- (Matt. 26:59; Mk. 15:1; Lk. 22:66; Acts 5:21,27,34,41; 6:12,15; 22:30; 23:1,15,20; 24:20)
B. Counselor (member of Sanhedrin) -- (Mk. 15:43; Lk. 23:50-53; Acts 5:34)
C. General terms used of those held in high regard -- people of importance
1. Elder -- (Matt. 15:2,3; Mk. 15:1; Acts 4:7; 24:1)2. Ruler -- (Jn. 3:1; 12:42)
D. High Priest
1. Annas and Caiaphas (son-in-law of Annas, Jn. 18:13) -- (Matt. 26:3,4,57-67; Lk. 3:2; Jn. 11:49-51; Acts 4:6; 5:17,18)2. Ananias -- (Acts 23:2-5; 24:1; 25:1-3)3. Unnamed -- (Acts 9:1,2)
E. Chief priests (A term referring to higher ranking priests who composed the leading opposition to Jesus.)
F. Ordinary priests -- (Lk. 1:5,9; Acts 4:1,2; 6:7)
G. Rabbi (general term for teacher/master) -- (Matt. 23:6-8; Jn. 1:38; 3:2,26)
H. Scribe (interpreter of the law) -- (Matt. 5:20; 7:29; 16:21; 20:18,19; 21:15; Mk. 2:5-7, 16; 12:38-40; 14:1; Lk. 6:7; Jn. 8:3,4; Acts 23:9; I Cor. 1:20)
I. Lawyer (doctor of the Jewish law) -- (Matt. 22:35,36; Lk. 2:46,47; 5:17; 7:29,30; 10:25-29; 11:45-52; Acts 5:34) (cf. I Tim. 1:7)
J. Captain of the temple -- Acts 4:1,2; 5:24-26; Sub-captains -- (Lk. 22:52)
K. Ruler of the synagogue (in charge of synagogue worship/procedure)
1. Crispus -- (Acts 18:8)2. Sosthenes -- (Acts 18:17)
IV. PLACES OF WORSHIP AND ASSEMBLY
A. Temple -- Herod's temple (begun in 20 B.C. and completed in 26 A.D., during the lifetime of Christ)
1. The temple complex -- (Matt. 21:12-14; 23:16,17,21; 24:1; Mk. 11:11; 15,16; 12:41; Lk. 2:46; 21:5,6; 24:53; Jn. 2:19-21; 8:20; Acts 2:46; 3:1-3, 7-10; 5:20,21,42; 21:26-30; 24:6)2. The sanctuary itself -- (Matt. 27:51) (cf. Mk. 15:38; Lk. 23:45) (I Cor. 9:13)3. The pinnacle -- (Matt. 4:5,6) (cf. Lk. 4:9)
B. The synagogue (local place of assembly)
1. Originated in Old Testament - (Ps. 74:8) (cf. Acts 15:21)2. A place where the law was read and where personal discourses were given -- (Matt. 13:54; Mk. 1:39; Acts 13:14,15; 14:1; 18:24-26)3. A place of disputation -- (Acts 6:9;17:1-3,17; 18:4; 19:8)4. Associated with being faithful to Judaism -- (Jn. 9:22; 12:42,43)
V. RELIGIOUS SECTS
A. Pharisees -- emphasized tradition, form, ritual -- (Matt. 5:20; 9:14; 15:1,2; 19:3; 23:1,2, 5-7, 13-16,23,25,27,29-31; Lk. 18:10-12; Jn. 3:1; Acts 15:5; 26:5) (cf. Phil. 3:5)
B. Sadducees -- aristocratic, wealthy, rejecting anything other than their definition of the law of Moses -- (Matt. 22:23; Acts 4:1,2; 5:17,18)
C. Pharisees and Sadducees mentioned together -- (Matt. 3:7; 16:1,6; Acts 23:6-9)
D. Herodians (a political group strongly promoting paying homage to Rome) -- (Matt: 22:15-17 (cf. Mk. 12:13) (Mk. 3:6)
E. Libertines (Jews who had been set free from the captivity under Pompey) -- (Acts 6:9)
VI. FEASTS
A. Feast of the Passover -- (Matt. 26:17-19; Lk. 2:41-43; Jn. 2:13-16;11:55-57; 18:28,39; Acts 12:3,4; 20:6)
B. Feast of Pentecost -- (Acts 2:1; 20:16; I Cor. 16:8) (see Lev. 23:15,16)
VII. OBSERVANCES
A. Sacrifices, offerings -- (Matt. 5:23,24; 8:3,4; Lk. 2:22-24)
B. Circumcision -- (Lk. 2:21; Jn. 7:22-24; Acts 15:1,5,24; 16:3; Gal. 5:2,3; Phil. 3:5)
C. Sabbath -- (Matt. 12:1,2,10-12; Lk. 14:1-6; Jn. 5:16)
D. Meat, drink, holy days -- (Gal. 4:10,11; Col. 2:16,17)
VIII. TRADITION AND RITUAL
A. Washing hands -- (Matt. 15:1,2; Mk. 7:1-4(a); Lk. 11:37,38)
B. Washing cups, plates, etc. -- (Mk. 7:4,8,13; Lk. 11:39)
C. Fasting -- (Matt. 6:16-18; 9:14; Lk. 18:12)
D. Tithing (inexpensive items) -- (Matt. 23:23; Lk. 11:42)
IX. SOCIAL ATTITUDES
A. Jewish pride and preeminence -- (Matt. 15:21-28; Jn. 4:7-9; 8:48; Acts 10:28)
B. Looking down on "sinners" -- (Mk. 2:14-16; Lk. 15:1,2; 18:11; 19:5-7)
C. The elite's desire for recognition -- (Matt. 23:5-7; Lk. 14:8-11)
D. Respect of persons -- (Jam. 2:1-9) (cf. Acts 10:34; Rom. 2:11; Gal. 2:6; Eph. 6:9; Col. 3:25; I Pet. 1:17) -- no "respect of persons" with God)
X. EDUCATION
A. School of higher learning -- (Acts 22:3) (cf. Acts 5:33-40)
B. Tutoring -- (Gal. 3:24,25) (schoolmaster)
XI.WEDDINGS
A. Important to have many guests -- (Matt. 22:1-3, 8-10; Jn. 2:1,2)
B. The bridegroom's friend (attendant) -- (Jn. 3:28,29)
C. An elaborate procedure -- (Matt. 25:1-12)
XII. BURIAL
A. Wealthy -- (Matt. 27:57-60) (cf. Is.53:9); Lk. 16:22; Jn. 19:39-42; Acts 13:29)
B. Common people -- (Matt. 14:12) (cf. Mk. 6:29); Acts 5:6,9,10; 8:2)
C. Outcasts -- Matt. 27:6-10 (cf. Acts 1:19)
XIII. PERSECUTION OF CHRISTIANS
A. Prophesied by Christ -- (Mk. 13:9; Jn. 15:20,21; 16:2)
B. Of apostles -- (Acts 4:13-21; 5:17,18, 26-33)
C. Of Stephen -- (Acts 6:8-15; 7:54 -- 8:1(a); 11:19)
D. Of household of Jason -- (Acts 17:5-9) (cf. I Thess. 2:18)
E. Of Paul -- (Acts 9:23,29; 14:1,2,5,19; 23:12,13; II Cor. 11:24-26; II Tim. 3:10,11)
F. By Paul -- (Acts 7:58; 8:1,3; 22:4,19,20; 26:9-11; Gal. 1:13,23; I Tim. 1:12,13)
XIV. DOCTRINAL INFLUENCE ON CHRISTIANITY -- (Acts 15:5,10,24; Gal. 1:6-9; 2:4; 3:1-3; 4:9-11; 5:1-4; Col. 2:16,17,18; I Tim. 1:3-7; Tit. 1:10-14) (cf. angel worship -- Col. 2:18)
XV. REBELLION AGAINST ROME -- (Matt. 22:17) (cf. Mk. 12:14; Lk. 20:22); Acts 5:37
XVI. FALL OF JUDAISM
A. Prophesied by Christ -- (Matt. 23:37,38; 24:15-22; 24:34; Lk. 21:20-24)
B. Paul's allusion to it -- (Heb. 10:25)
Note: This outline does not contain many other things found in the New Testament that were a known part of the first century world. For example: references to cities, regions, countries, islands, rivers, seas, lakes, mountains, hills, valleys and structures. All of these add to the extensive nature of the New Testament record.
| Powered By |
| TheLordsWay.com |
| Click here to host your own church web site today! |

